Default Permissions
DCM can set default permissions for objects by naming them access objects. Access objects are grouped by type.
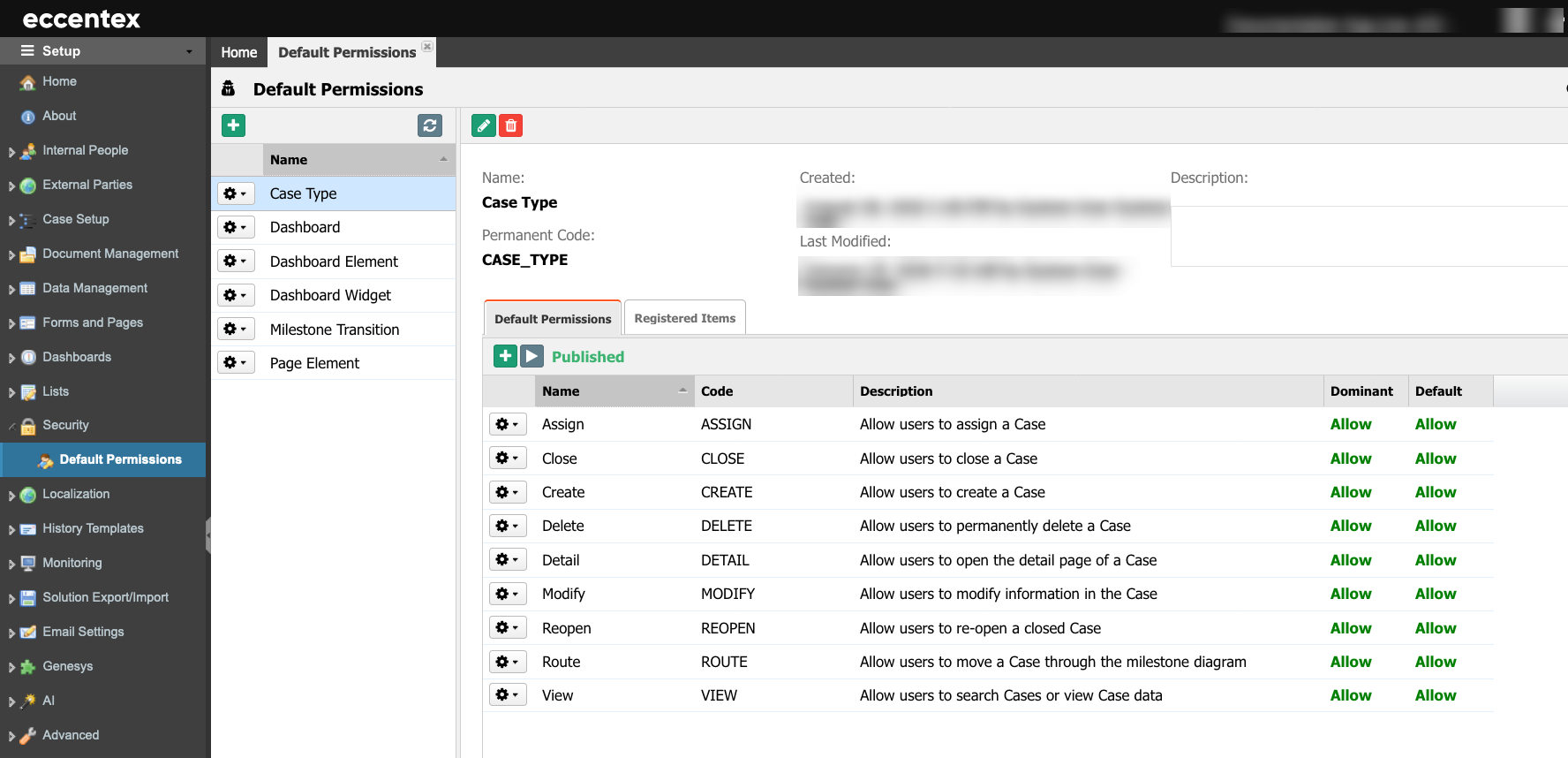
Default Permissions
The table below describes the list of implemented access object types and a set of default permissions for actions.
| Access Object Type | Default Permission for Action | Note | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Case Type | Assign, Create, Close, Delete, Detail, Modify, Reopen, Route, View | Case workflow |
| 2 | Dashboard | View | Permissions for a dashboard. It is not applied to personal dashboards |
| 3 | Dashboard Element | Enable, View | Permissions for a dashboard element. It doesn't apply to personal dashboards |
| 4 | Dashboard Widget | View | Permissions for a dashboard widget |
| 5 | Milestone Transition | Execute | Permissions for transitions on milestone builder. It affects the visibility of routing buttons on Case detail pages. |
| 6 | Page Element | Enable, View | Permissions for a page element. They are acceptable for all types of detail page |
Dominant Settings
Dominant setting defines the dominant permission setting through all unit permission settings. Dominant Permission is highly important if unit permissions are set.
The default setting defines the default value of each permission. Default Permission is a high priority if unit permissions are not set.
The unit is a grouped list of users named Team, Business Role, or Skill.
How dominant and default settings work. The following example demonstrates the security matrix access for objects against units for common cases.
| Access Object Type | Action | Dominant | Default | Result |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Case Type | Create | Allow | Deny | NOT DISPLAYED |
| Deny | Allow | DISPLAYED |
The same behavior applies to other access object types and their actions.
