Relationships
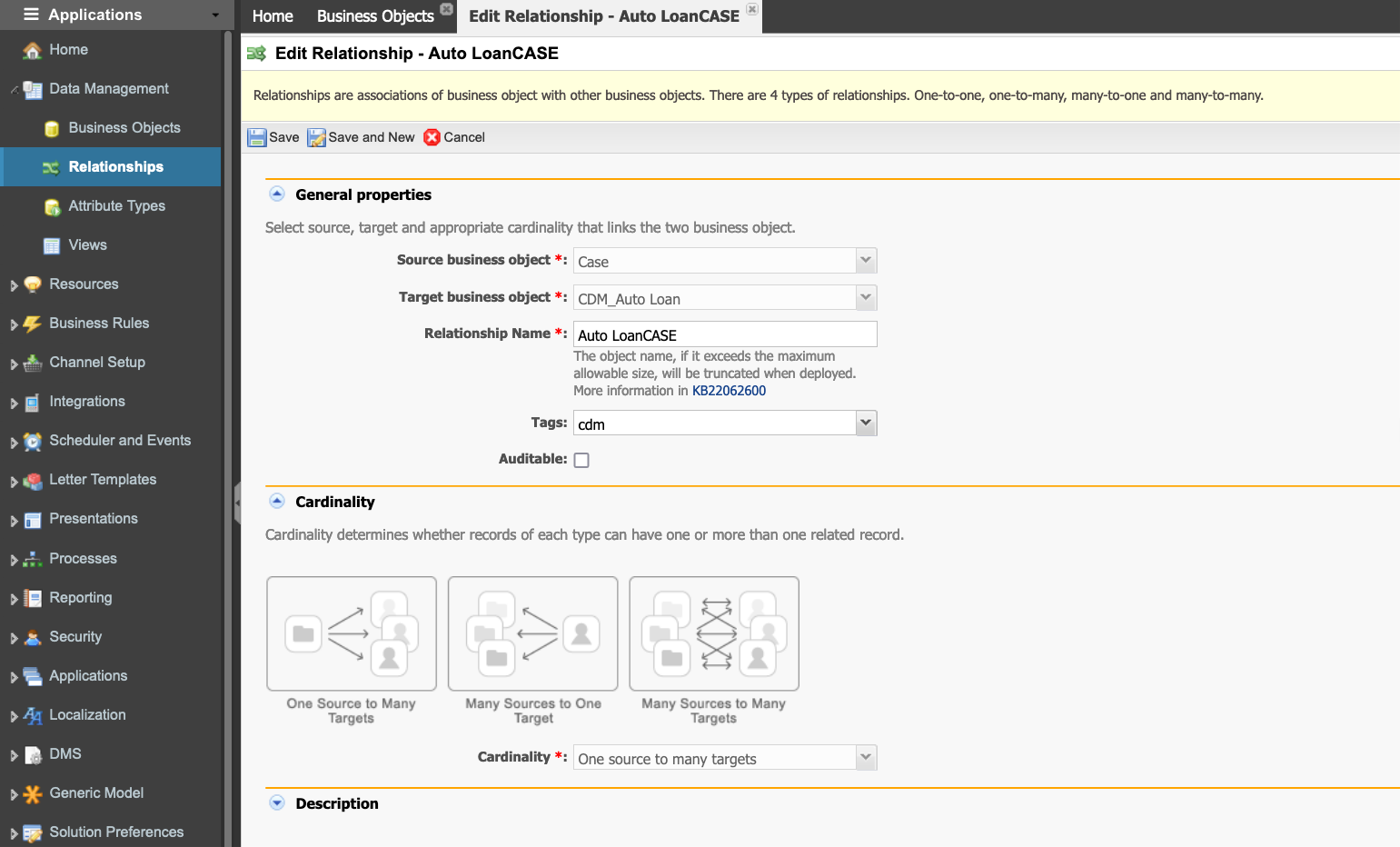
A Relationship can be established between two business objects so that data can be split and stored in different objects. For example, you can relate a Customer to an Order, an Order to a Product Part, and a Product Part to a Product Suite. Two types of relationships can be configured (also known as cardinality rules):
One source to many targets: Relates one object (source) to potentially many other business objects (targets). For example, you might use this option to relate one case manager to many cases or one record in one business object to many records in another.
Many Sources to one target: This is the inverse of the option above. For example, you might use this option to relate many documents to one folder.
Articles
